
{{cart_num}}
My CartTel: +86 010 50973105
FAQ—Solarbio Dye Reagents
FAQ Documentation—Dye Reagents
| Q01: | How many slides can a box of dye make? Or the customer has 50 samples,how much dye solution is needed? |
| A01: | The number of times the reagent is used is affected by the properties of the solute or solvent. Taking the general water-soluble neutral dyeing solution as an example,it is recommended to add 200-400ul to cover the tissue for each tissue section dyeing. It is recommended to use 0.5ml for each hole of 24-well plate and 1ml for each hole of 6-well plate. That is,20ml can be used to make about 80 tissue sections,about 40 times for 24-well plates and about 20 times for 6-well plates. A simple algorithm can also be used for cell staining estimation,that is,a hole plate staining requires a total of about 6ml of staining solution. On the one hand,the reagent is easily contaminated by the previous treatment reagent or cleaning solution during the dyeing process,resulting in a shorter validity period. On the other hand,some reagents need to be in a special state (supersaturated,highly activated,excited state) to be better dyed,which needs to be used now and cannot be recycled. For high-throughput dyeing requirements and some dyeing solutions that can be impregnated,the optimal section bearing capacity of a cylinder of dyeing solution can usually be calculated according to 1ml/ section,and the actual carrying capacity needs to be estimated according to different maintenance degrees,usually between 0.8 times and 2.5 times. |
| Q02: | Can the dye kit do plant samples or bacteria or fungi? |
| A02: | There are special plant dyeing solution and microbial dyeing solution can be selected,and the conventional dyeing kit is still mainly to stain mammalian tissue sections or cell smears. The specific dyeing needs of special samples can consult 400-968-6088 to 2 consulting technical support to confirm the dyeing scheme that more meets your needs. |
| Q03: | Can the staining kit stain cells? |
| A03: | First of all,it is recommended to look at the manual,the general manual,generally can be dyed,but it is still recommended to adjust according to the experimental results. Some of the kits we marked cell specific,can do cell,it is recommended to do a pre-experiment. |
| Q04: | What are the elastic fiber dyeing kits? |
| A04: | The matching kit for elastic fiber dyeing is G1589/G1593/G1596/G1598,and the single dyeing solution is G1588/G1592/G1594/G1922. For specific dyeing methods and results,please search the corresponding item number on the official website. |
| Q05: | What are the fiber staining kits (connective tissue staining kits)? |
| A05: | Connective tissue multi-color dyeing kit has G1340/G1343/G1346 G1355/G1472 G1590/G1591/G1595/G1597/G2040/G3500/G3550/G3701 G1340 G1343/G1346 for Masson three color Dyeing method is used to distinguish collagen fibers from muscle fibers. G1340 is a classic dyeing method,which can dye muscle fibers red and collagen fibers blue. G1343/G1346 is an improved method based on G1340. G1343 uses solid green instead of aniline blue,which can dye muscle fibers red and collagen fibers green. G1346 adds mordant component,can better distinguish muscle fiber and collagen fiber dyeing,and is not easy to overstain. G1355 is Mallory three-color staining method without nuclear staining solution. After our improvement and optimization,the staining is constant and consistent,and the dyeing results of muscle fiber and collagen fiber are the same as those of classical Masson staining method. G1472 is a modified VG method,which does not contain picric acid and can dye muscle fibers yellow and collagen fibers red. G1590/G1591/G1595/G1597 to improve the EVG staining method,combined with G1472 and G1592/G1596/G1598 dyeing kit,so as to distinguish the collagen fiber and elastic fiber dyeing. G2040/G3500/G3550/G3701 is a derivative of the classic Masson staining method and can be used with other dyes for the staining of cellulose,plaques,proteoglycan,new bone and mineralized bone. |
| Q06: | What are the kits for reticular fiber dyeing? |
| A06: | Kit for reticular fiber dyeing is G3525/G3535,single reagent is G3520/G3530. G3525 Using the modified Gordon-Sweets method,G3520 is the main stain for G3525,which can dye the mesh fibers reddish-brown to black,and the collagen fibers yellow to yellow-brown; G3535 uses the modified Gomori ammonia-silver process,and G3530 is the main stain of G3535,which can dye the reticular fibers reddish-brown to black,and the collagen fibers yellow to yellow-brown. |
| Q07: | What are the kits for muscle fiber dyeing? |
| A07: | The muscle fiber dyeing kit is divided into Mallory phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin staining series (G1380/G1381/G1382/G1383) and Puchtler azo fluorescence peach method (G3470/G3475). G1380 and G1381 use naturally oxidized phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin,long maturation time,shelf life can be up to 2 years; G1382 and G1383 use the chemical oxidation of phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin,maturation time is short,shelf life is short only 3 months,can be striated muscle,cellulose and other dark blue. G3470 uses Puchtler fluorescent pink method) can stain the muscle fibers red,and the rest tissues are yellow to different degrees. G3475 is the main stain of G3470,and the dyeing results of the muscle fibers are the same as G3470. |
| Q08: | What are the Nissl staining kits? |
| A08: | He's dyeing related products have G1430/G1432/G1434/G1436/G1438,tar purple method,methyl violet method respectively,methylene blue and toluidine blue,sulfur method,pansy according to austenite basophilic,austenite can be dyed blue to violet,background is colorless or light blue. |
| Q09: | How to choose the specifications of the dye solution kit? |
| A09: | First of all,it is necessary to calculate the volume of dyeing liquid required according to the sample size. For some dyeing liquid with short dyeing time and non-volatile dyeing,the drip dyeing method can be adopted. As long as the drip adding amount covers the sample,it is not recommended to recycle after dyeing. However,for some dyeing liquid with long dyeing time and easy volatilization,it is necessary to adopt the method of immersion dyeing. The amount of dyeing liquid in the upright section box with 5 sheets is not less than 15ml,and the amount of dyeing liquid in the dyeing tank with 25 sheets is not less than 150ml. The immersed dyeing liquid can be reused 3-5 times in general,except for the reagent that can not be recycled and used. The actual number of repetitions needs to be determined according to the dyeing effect,if the dyeing effect is significantly reduced,you need to discard the dye. |
| Q10: | Can you use paraffin sections,frozen sections or tissue samples according to the operating steps on the instructions of some dyeing kits? |
| A10: | The commonly used sample of our staining kit is paraffin section. The operation procedure of frozen section and cell sample is not written in the manual,which does not mean that it cannot be done. First of all,you can refer to the relevant literature to see whether the staining method is used in frozen section or cell sample dyeing,and then do a preliminary experiment before the formal experiment in large quantities. Adjust and optimize the optimal dyeing procedure according to the results of the pre-experiment. If you cannot find the relevant literature,you can call 400-968-6088 to 2 for technical consultation. |
| Q11: | I dyed exactly according to the instructions of the dyeing solution,why didn't I get the result? |
| A11: | First of all,our kit verification samples are limited,involving special sample dyeing results do not match the expectations of the case,you can call 400-968-6088 contact our technical support or fill in the feedback report to send to the technical email,technical support to assist you to solve the relevant problems according to the actual test situation. Secondly,if you feel that the after-sales cycle is long,you want to confirm and optimize the results by yourself,you can refer to the following scheme or provide the scheme involved data to technical support 1. Check the relevant literature to confirm whether the accuracy and scope of application of the kit experimental scheme meet the experimental requirements,such as the conventional bivalent iron dyeing kit is not suitable for all iron death dyeing tests. 2. Confirm the successful modeling of the experiment by other indicators,such as cell growth arrest induced by D-galactose or hydrogen peroxide,and some cells show comet-like morphological changes,and then the age-related galactosidase can be stained positive. 3. There are strict restrictions on ion types,osmotic pressure and temperature of tissue treatment solution before and after special enzyme activity staining. For example,phosphoric acid will inhibit alkaline phosphatase activity,while non-specific interference will occur to most metal precipitation staining schemes; decalcified solution treatment will lead to no positive calcium salt staining; tap water treatment will lead to water-soluble eosin decolorization,etc. 4,due to the different steps of tissue sampling,fixation,embedding and so on,the dyeing results will also be different to a certain extent,you can confirm with our technical support whether the relevant steps affect the dyeing results. 5,all the dyeing results are for the test service,so in addition to the standard dyeing results,specific positive substances can be targeted according to the experimental needs. This adjustment is normal operation and does not involve falsification or manipulation of experimental results. |
| Q12: | masson tricolor aniline blue color is relatively light how to do? |
| A12: | masson trichromatic dyeing principle is mainly to color the fibers according to the molecular weight of the dyes,aniline blue molecular weight is relatively large,it is not easy to infiltrate into the fibers,so if aniline blue color is relatively light,aniline blue dyeing time can be extended,and phosphomolybdic acid is the medium of aniline blue coloring,it can also extend the processing time of phosphomolybdic acid,but it should be noted that,If aniline blue is too dark,it will affect the observation of other colors. Please adjust the dyeing time according to the actual result. |
| Q13: | How to prepare cell smear? |
| A13: | Fresh whole blood or anticoagulant whole blood can be directly dripped at one end of the slide with 5ul,then pushed away at a 30-45 degree Angle with another slide,dried for 3-5min,then dripped with methanol or ethanol and fixed for 1-3min to prepare the smear. Separation solution for cell purification and cell lavage collection cells must be centrifuged first,then washed,and the cells are prepared into a single-cell suspension with a buffer solution mixed with ionic colloid. 5-10ul cell suspension drops are placed on one side of the slide,and cell smear is prepared by pushing the cover slide and the slide at a 30-45 degree Angle. Then make a mark,dry,fixed,after the follow-up specific dyeing experiment. Cell density requires several more attempts to achieve the best results. |
| Q14: | What is the difference between frozen section and paraffin section? |
| A14: | 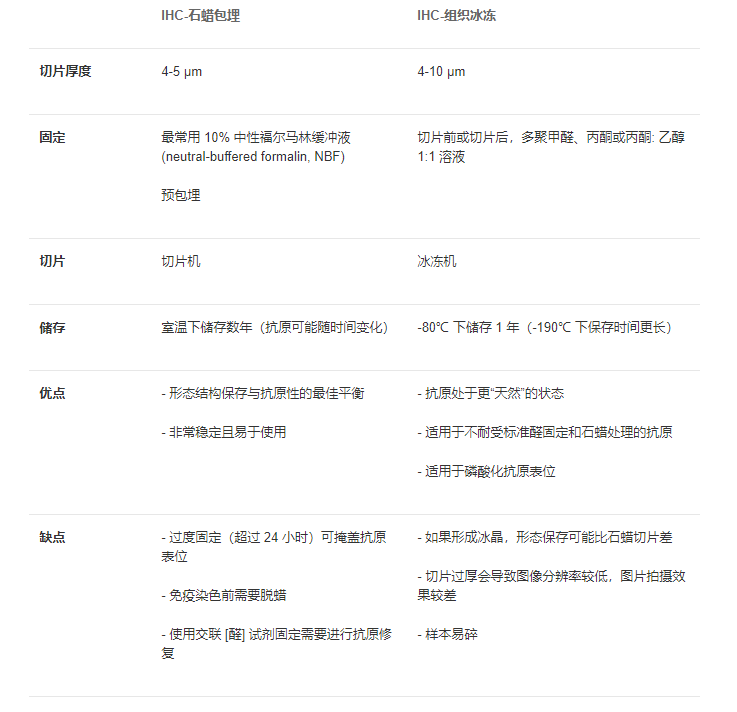 |
| Q15: | Summary of frequently asked questions about hematoxylin and eosin in HE staining. |
| A15: | HE staining is a common staining method in histomorphologic observation,where hematoxylin is an alkaline dye that can stain acidic proteins and nucleic acids,and is usually used to stain the nucleus. Eosin is an acidic dye that colors basic proteins in the cytoplasm of cells. The color of hematoxylin is usually blue to blue-purple,and if the color of hematoxylin is too deep and black during the dyeing process,it can be adjusted by shortening the dyeing time of hematoxylin or appropriate differentiation. If the color is red or lighter,the hematoxylin staining time can be appropriately prolonged,the differentiation time can be shortened and the return blue time can be prolonged. Eosin is usually colored pink to rose red. Water soluble eosin is bright in color,but it is easy to be decolorized by tap water and low concentration ethanol. Alcohol soluble eosin is not easy to decolorize,but the overall color is lighter and slightly yellowish. For different use needs,our company has prepared four ready-to-use HE dyeing reagent sets,you can choose the right products according to your specific needs. G1120 is a classic HE staining combination,the overall color is light,does not contain alcohol,can be used for conventional dyeing and IHC double dyeing. G1121 is to strengthen the HE dyeing combination,the overall color is deep,resistant to cleaning,the result is bright and durable,can be used for HE dyeing alone or teaching. G1126 is a high-throughput HE dyeing combination. Based on G1120,more stabilizing reagents are introduced to adapt to the working conditions of the dyeing agent. The overall coloring is moderate,and it can withstand the cleaning and differentiation of the general process. G4520 is a one-step HE staining reagent,which is convenient for rapid staining observation in temporary laboratories. |
| Q16: | What is the general method and process of paraffin section preparation? |
| A16: | Paraffin section mainly includes the following steps: perfusion (optional),sampling,fixation,decalcification/softening (optional),dehydration,transparency,wax dipping,embedding,section. Specific steps here only do a simple description more specific introduction can refer to:General tissue paraffin section preparation procedure refer to perfusion (optional): Brain tissue or large animal samples are usually difficult to be fully fixed by soaking,so it is necessary to use materials after perfusion and fixation in advance. Sampling: Tissue sampling should be done as soon as possible,while avoiding sampling damage such as tweezers and scratches in the sample area. After sampling,the excess blood water should be washed with normal saline,immersed in fixed solution or non-woven cloth to absorb excess water,and then frozen. Fixation: The tissue cells after sampling are still in a living state,which will produce changes that do not meet the needs of the experiment. The fixation solution is to stop the living state of the cells,and to keep it as far as possible at the moment of sampling for experimental analysis. Decalcification/softening (optional) : Paraffin embedding is based on paraffin wax. In order to ensure uniform section,it is necessary to ensure that the tissue hardness is the same as or slightly lower than that of paraffin wax. High hardness components such as bone,keratin and implants without softening or decalcification can result in a broken knife or scratched tissue section. Dehydration: conventional tissue has a large water content,which is easy to deform and distort and promote cell autolysis. Dehydration can strengthen the stability of cell structure and further inhibit enzyme activity to fix the cell state. Transparent: Because ethanol and paraffin are not miscible,the dehydrated tissue needs to be infiltrated and replaced by a transparent agent before wax embedding. Xylene is a common transparent agent. In recent years,the transparent dewaxing solution of environmental protection organizations is commonly used to replace xylene for transparency. Wax dipping: step by step wax dipping is to gradually replace the transparent agent in the tissue,so that the tissue is fully supported by paraffin infiltration,which can effectively avoid the collapse and cracking of the tissue after embedding. Embedding: The tissue is washed with pure paraffin wax,moved to the embedding box,and condensed into a uniform paraffin embedding block. Proper freezing in the -20℃ refrigerator before slicing can improve the hardness of the wax block and optimize the slicing effect. |
| Q17: | Can hematoxylin dye still be used with precipitation? |
| A17: | If there is a small amount of precipitation or a layer of metal oxide film floating above the newly opened or newly poured hematoxylin dyeing solution overnight in the newly opened or dyeing tank,it is a normal phenomenon caused by natural oxidation in the storage process,and can be used after filtering with qualitative filter paper without affecting the use of normal production. If a large amount of precipitation or metal film is formed soon after long-term use,the dyeing effect attenuates obviously,it is recommended to replace the dyeing solution. |
| Q18: | What is the difference between G1010 Jemsa dyeing solution (working solution) and G1015 Jemsa dyeing solution (10* stock solution)? |
| A18: | The G1010 is a ready-to-use package with both concentrate and diluent. The product G1015 only has dyeing solution (10×),diluent needs to be prepared or purchased separately. |
| Q19: | G1020 Reichs-Giemsa composite dye dyeing effect is not good what reason? |
| A19: | The staining solution is sensitive to pH and has a good display effect on the nucleus and cytoplasm at pH6.6-6.8,that is,in a general sense,a good staining effect needs to be diluted and cleaned with a buffer of pH6.6-6.8,and observed under the mirror with the buffer or dry (the nucleus is purplish red to blue-purple,and the cytoplasm is usually pink). If you need to focus on nucleated cells or nuclear coloring,you can use a buffer solution with a PH of 7.2-7.4 (blue to blue-purple nuclei,light blue or no coloring of cytoplasm). In addition to pH,the degree of cell stretch will also affect the observation effect to a certain extent. For cell samples obtained with separation solution or lavage solution,it is recommended to use a mixture of ion and colloid isotonic liquid to prepare smear,and fully rehydrate after fixation to avoid large differences between the nucleocytoplasmic ratio and normal state. |
| Q20: | What are the common nuclear staining solutions? |
| A20: | Commonly used nuclear optical dye solutions are hematoxylin (blue-purple),nuclear solid red (red),crystal violet (purple),methyl green (green) and so on. Fluorescent staining solutions include DAPI (blue-purple fluorescence),Hoechst 33342 (blue-green fluorescence),Hoechst33258 (blue-green fluorescence),and PI (red fluorescence). |
| Q21: | Hoechst 33342,Hoechst33258 What is the difference between these two fluorescent dyes? |
| A21: | The two dyes have the same thing in common is that they can bind to nucleic acids,and then stain the nucleus,and the fluorescence after excitation is blue. The difference is that Hoechst 33342 can stain the nuclei of living and dead cells through the cell membrane,while Hoechst33258 is better for staining cells after fixation. |
| Q22: | What are the problems that need attention in the general dyeing process? |
| A22: | ① It is recommended to carefully read the instructions before dyeing to ensure that the dyeing reagent is properly stored to avoid the failure of the reagent caused by preservation. ② Some dye solutions need to be used on the spot,or filtered before use,and must be accurately treated according to the instructions to avoid affecting the experimental results. ③ The dyeing process in addition to the need to grasp the dyeing time but also control the cleaning time,batch dyeing must try to ensure that the first and last processing interval time does not exceed 20s,to avoid the operation caused by the same batch of tissue dyeing uneven. ④ In the dyeing process,try to use distilled water for cleaning operations. Buffer or tap water may cause some pH specific binding dyes or specific ions to inhibit enzyme activity,resulting in dyeing results that are not as expected. Not all dyeing solutions have an additive effect (the longer the dyeing time,the better),and some competitive dyeing or progressive dyeing reagents must strictly control the dyeing time. ⑥ The sections with special staining usually need to confirm the correctness and specificity of the staining results against the pictures. When it is difficult to determine the specificity of the results with large areas,at least one adjacent section is selected for HE control staining as the basis for the identification of tissue morphology. 7 Tissue dry tablets will lead to changes in the tissue's adsorption of dyes and it is difficult to remove trace bubbles,which will affect the observation of the results,so in the dyeing process,the non-special requirements of the scheme must be avoided as far as possible. ⑧ Not all dyeing solutions can be recycled,such as the manual label is difficult to meet the actual experimental dyeing needs,it is recommended to call 400-968-6088 for technical support. |
| Q23: | Can crystal violet dye be diluted? What is the difference between these crystal violet stains? |
| A23: | C8470 is crystal violet dye powder,customers can be configured according to their own needs into different concentrations and different uses of crystal violet dyeing solution. G1061,G1062,G1063 are ammonium oxalate crystal violet dyeing solution,the concentration is different,these three are composite dyeing solution,generally used for Gram or bacterial polysaccharide dyeing,the solvent is complex can not be directly diluted use,customers can choose different concentrations of dyeing solution according to their needs. The rest of the dyeing solution,a single solvent (water,alcohol,etc.) with crystal violet solution,useful buffer components (citric acid,glycine,etc.) with crystal violet dyeing solution,suitable for different uses can be selected according to their own needs. |
| Q24: | What is the difference between D8200,C0060 and C0065? |
| A24: | D8200 is a dry DAPI dye powder that can be dissolved directly in sterile water and used in the required concentration. C0060 DAPI solution (1mg/ml) is a DAPI reserve solution with a prepared concentration of 1mg/ml,which can be diluted and dyed according to the instructions when used,without weighing and dissolving. C0065 DAPI solution (readyuse) 10ug/ml is a readyuse dye that can be dyed directly without dilution. |
| Q25: | What is the difference between G1260,G1261,G1262,G1263,G1264 oil red O dye? |
| A25: | G1260 is a saturated oil red O reserve dye,can not be used alone for dyeing,often do kit refill. G1261 is a readyuse oil red O staining kit,which does not contain fixed solution,but contains oil red O dyeing solution and hematoxylin redyeing solution,mainly used for tissue section dyeing. G1262 is a ready-use oil red O staining kit for cell lipid drop staining,which contains fixative,oil red O staining solution and hematoxylin staining solution. G1263 is an environmentally friendly readyuse oil red O dyeing kit with no need to prepare working liquid,less precipitation and low volatilization,which can be used to replace conventional oil red O dyeing kit. G1264 is a read-to-use fluorescent dyeing kit for lipids. It basically does not contain organic solvents and has little effect on the position of lipid droplets. It has high staining accuracy,but requires fluorescence microscopy for observation and imaging. |
| Q26: | What is the cause of precipitation in the dyeing process of oil red O dyeing solution? |
| A26: | The oil red O dyeing working liquid itself is a supersaturated solution,so it is easy to precipitate. The working liquid is recommended to be prepared on the spot,prepared and placed for 10-15min,filtered to remove precipitation and then dyed. |
| Q27: | Why the product just opened the dyeing effect is good,opened for a period of time,the dyeing effect is not good,but the product is still in the shelf life? |
| A27: | The shelf life of the product refers to the shelf life of the product in the unopened state. Once the product is opened,unpredictable reactions will occur due to a series of problems such as humidity or contact with air,thus affecting the stability of the product. Therefore,the shelf life of the product after opening is usually treated by half,it is recommended to avoid long-term exposure and use up the product as soon as possible after opening. |
| Q28: | How to configure hematoxylin powder into hematoxylin dyeing solution? |
| A28: | The formula of our hematoxylin dyeing solution is confidential and it is not convenient to make it public. You can prepare it by referring to the formula of hematoxylin in the literature,or buy our prepared hematoxylin solution directly. |
| Q29: | G2510- Can eco-friendly transparent dewaxing solution completely replace xylene? |
| A29: | This environmentally friendly transparent dewaxing solution can directly replace xylene as a transparent agent and dewaxing agent in the process of tissue waxing and section dewaxing. The compatibility of the sealing agent needs to be tested before section sealing. Tissue sealing tablets are composed of xylene products in the market,and some products may be incompatible with environmentally friendly dewaxing agents. It is recommended to mix an equal amount of dewaxing solution with existing laboratory sealing tablets before use. If no turbidity is produced,it can replace xylene for transparency before sealing tablets. We also have G8593- odorless benzene free neutral gum,can replace the conventional xylene neutral gum used for sealing,and compatible with environmental organizations transparent dewaxing agent. |
| Q30: | Alizarin red different PH values how to choose? |
| A30: | Alizarin red is mainly used to stain calcium salts in cells or tissues. For tissues or cells with relatively low salt content,this dye with PH 8.3 can be selected. Calcium salts are easily decomposed in acidic PH environments,resulting in false negative results. |
| Q31: | What problems should be paid attention to in the process of fluorescent dye dyeing? |
| A31: | Fluorescent dyes are easy to quench,so it is necessary to pay attention to the operation of avoiding light during the dyeing process. Some fluorescent dyes are not easy to stain during the dyeing process,and cells or tissues can be permeated with permeability to make it easier to stain. |
| Q32: | What is the difference between jc-1 and jc-10 mitochondrial membrane potential fluorescence probes? |
| A32: | Both of them are probes for detecting mitochondrial membrane potential. jc-10 is further developed on the basis of jc-1,and jc-10 is more water-soluble and more stable. |
| Q33: | Why do you buy the same number of dyeing liquid,the dyeing effect of large specifications is not as good as that of small specifications? |
| A33: | Some dyeing solution is stored at low temperature,and some dyeing solution coloring and temperature is related,in this case,the large size of the dyeing solution to restore to room temperature time is longer than the small size of the time,if the temperature is not enough will affect the coloring effect. |
| Q34: | Fat tissue oil red O staining is less positive,there are vacuoles,what is the reason? |
| A34: | Fat cells in the tissue are large,and the conventional 10um section is easy to cut,resulting in the exposure of fat droplets and then drift,forming vacuoles. The section thickness can be adjusted to 15um or 20um. Fat cells are fragile,so avoid pressing the tablet when sealing the tablet after staining. Pressing the tablet may also crush the fat cells and cause the leakage of fat droplets. |
| Q35: | Why does the tissue stain unevenly after staining? |
| A35: | It may be due to the following reasons: 1. The thickness of the section is not uniform or the tissue dewaxing is insufficient,resulting in some ar eas are not colored. 2. More residual reagents lead to insufficient contact between the staining solution and the tissue. 3. The staining solution fails to completely cover the tissue and exceeds the edge by 2-3mm,resulting in uneven staining of the edge. 4. Continuous treatment of multiple sections or use of volatile reagents such as ethanol to treat sections leads to section drying during the dyeing process. 5. The sample is special molding,and the dyeing results are not uniform. Control discrimination methods are as follows: 1. HE staining is performed on adjacent sections to observe whether the staining is uniform. If HE staining is also uneven,problems related to tissue sampling or section preparation are given priority. 2. If the staining is uneven and obvious round drops or tangential lines appear,consider the reasons for more residual reagents or dry flakes. 3. If the staining results appear obvious edge and middle inconsistency,consider whether the fixation is sufficient and edge effect. |
| Q36: | What is the difference between G1281,G1280,G1360 and G1282 glycogen staining kits? |
| A36: | G1280 contains only oxidants and Schiff's reagent,and can only stain glycogen or polysaccharide. G1281 added an additional hematoxylin redye solution for interlining tissue morphology. G1282 contains hematoxylin in addition to amylase,can prepare glycogen negative control,to avoid the influence of tissue polysaccharide or glycosaminoglycan on the judgment of glycogen content. G1360 adds fixing solution and reducing agent on the basis of conventional dyeing,which is used to meet the special needs of cell dyeing. |
| Q37: | P1126,P1127 two Gluta fixative color yellow can still be used? |
| A37: | The Gluta fixative received is slightly yellow in color and can be used normally. Due to the nature of the product itself is more prone to self-polymerization to form a slightly yellow intermediate,so the phenomenon of yellowing will occur when placed for a period of time,but it does not affect the use effect. Obvious Browning is not recommended. |

